本文介绍了“如何使用属性”的知识。很多人在实际案例的操作中会遇到这样的困难。接下来,让边肖带领大家学习如何应对这些情况!希望大家认真阅读,学点东西!
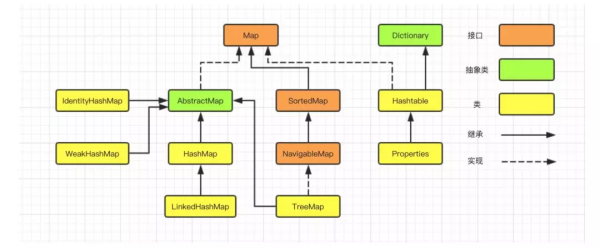
00-1010map实现类包括HashMap、LinkedHashMap、TreeMap、IdentityHashMap、WeakHashMap、Hashtable、Properties等。
01. 摘要
Properties类是java工具包中一个非常重要的类。例如,在实际开发中,一些变量可以直接写入自定义java枚举类。
但是,有些变量在测试环境、生产前环境和生产环境中需要不同的值。这时候我们可以利用属性文件加载程序所需的配置信息,从而达到一行代码可以在多种环境下运行的效果!
最常见的是JDBC数据源配置文件。属性文件以。属性,文件的内容以key=value格式编写,变量名在左边,变量值在右边。例如,创建一个新的jdbc.properties文件,内容如下:

属性类是属性文件和程序之间的中间桥梁。无论是从属性文件中读取信息还是将信息写入属性文件,都必须通过属性类。
好了,唠叨了这么多,还是回到本文要介绍的主角Properties吧!
从集合的Map架构图可以看出,Properties继承自Hashtable,表示一个持久的映射集合,属性列表以键值的形式存在。属性类的定义如下:
public class properties extendshashtableobject,对象{ 0....................

02. 简介
set 方法(添加修改元素)
set方法是向映射中添加指定的键和值对。添加元素时,调用Hashtable的put方法。与哈希表不同,键和值都是字符串。
打开Properties的setProperty方法,源代码如下:
public synchronized objectset property(String Key,String Value){//调用父类Hashtable returnput(key,Value)的put方法;}方法测试如下:
publicationstatinvitmain(String[]args){ properties properties=new properties();Properties.setProperty('name1 ','张三');Properties.setProperty('name2 ','张思');Properties.setProperty('name3 ','张武');n
bsp; System.out.println(properties.toString()); }
输出结果:
{name3=张五, name2=张四, name1=张三}
get 方法(搜索指定元素)
get 方法根据指定的 key 值返回对应的 value,第一步是从调用 Hashtable 的 get 方法,如果有返回值,直接返回;如果没有返回值,但是初始化时传入了defaults变量,从 defaults变量中,也就是 Properties 中,去搜索是否有对于的变量,如果有就返回元素值。
打开 Properties 的 getProperty 方法,源码如下:
public String getProperty(String key) { //调用父类 Hashtable 的 get 方法 Object oval = super.get(key); String sval = (oval instanceof String) ? (String)oval : null; //进行变量非空判断 return ((sval == null) && (defaults != null)) ? defaults.getProperty(key) : sval; }
查看 defaults 这个变量,源码如下:
public class Properties extends Hashtable<Object,Object> { protected Properties defaults; }
这个变量在什么时候赋值呢,打开源码如下:
public Properties(Properties defaults) { this.defaults = defaults; }
可以发现,在 Properties 构造方法初始化阶段,如果你给了一个自定义的 defaults ,当调用 Hashtable 的 get 方法没有搜索到元素值的时候,并且 defaults 也不等于空,那么就会进一步在 defaults 里面进行搜索元素值。
方法测试如下:
public static void main(String[] args) { Properties properties = new Properties(); properties.setProperty("name1","张三"); properties.setProperty("name2","张四"); properties.setProperty("name3","张五"); //将 properties 作为参数初始化到 newProperties 中 Properties newProperties = new Properties(properties); newProperties.setProperty("name4","李三"); //查询key中 name1 的值 System.out.println("查询结果:" + properties.getProperty("name1")); }
输出结果:
通过key查询结果:张三
load方法(加载配置文件)
load 方法,表示将 properties 文件以输入流的形式加载文件,并且提取里面的键、值对,将键值对元素添加到 map 中去。
打开 Properties 的 load 方法,源码如下:
public synchronized void load(InputStream inStream) throws IOException { //读取文件流 load0(new LineReader(inStream)); }
load0 方法,源码如下:
private void load0 (LineReader lr) throws IOException { char[] convtBuf = new char[1024]; int limit; int keyLen; int valueStart; char c; boolean hasSep; boolean precedingBackslash; //一行一行的读取 while ((limit = lr.readLine()) >= 0) { c = 0; keyLen = 0; valueStart = limit; hasSep = false; precedingBackslash = false; //判断key的长度 while (keyLen < limit) { c = lr.lineBuf[keyLen]; if ((c == '=' || c == ':') && !precedingBackslash) { valueStart = keyLen + 1; hasSep = true; break; } else if ((c == ' ' || c == '\t' || c == '\f') && !precedingBackslash) { valueStart = keyLen + 1; break; } if (c == '\\') { precedingBackslash = !precedingBackslash; } else { precedingBackslash = false; } keyLen++; } //获取值的起始位置 while (valueStart < limit) { c = lr.lineBuf[valueStart]; if (c != ' ' && c != '\t' && c != '\f') { if (!hasSep && (c == '=' || c == ':')) { hasSep = true; } else { break; } } valueStart++; } //获取文件中的键和值参数 String key = loadConvert(lr.lineBuf, 0, keyLen, convtBuf); String value = loadConvert(lr.lineBuf, valueStart, limit - valueStart, convtBuf); //调用 Hashtable 的 put 方法,将键值加入 map 中 put(key, value); } }
好了,我们来在src/recources目录下,新建一个custom.properties配置文件,内容如下:
#定义一个变量名称和值 userName=李三 userPwd=123456 userAge=18 userGender=男 userEmail=123@123.com
方法测试如下:
public class TestProperties { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //初始化 Properties Properties prop = new Properties(); //加载配置文件 InputStream in = TestProperties .class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("custom.properties"); //读取配置文件,指定编码格式,避免读取中文乱码 prop.load(new InputStreamReader(in, "UTF-8")); //将内容输出到控制台 prop.list(System.out); } }
输出结果:
userPwd=123456
userEmail=123@123.com
userAge=18
userName=李三
userGender=男
propertyNames方法(读取全部信息)
propertyNames 方法,表示读取 Properties 的全部信息,本质是创建一个新的 Hashtable 对象,然后将原 Hashtable 中的数据复制到新的 Hashtable 中,并将 map 中的 key 全部返回。
打开 Properties 的 propertyNames 方法,源码如下:
public Enumeration<?> propertyNames() { Hashtable<String,Object> h = new Hashtable<>(); //将原 map 添加到新的 Hashtable 中 enumerate(h); //返回 Hashtable 中全部的 key 元素 return h.keys(); }
enumerate 方法,源码如下:
private synchronized void enumerate(Hashtable<String,Object> h) { //判断 Properties 中是否有初始化的配置文件 if (defaults != null) { defaults.enumerate(h); } //将原 Hashtable 中的数据添加到新的 Hashtable 中 for (Enumeration<?> e = keys() ; e.hasMoreElements() ;) { String key = (String)e.nextElement(); h.put(key, get(key)); } }
方法测试如下:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //初始化 Properties Properties prop = new Properties(); //加载配置文件 InputStream in = TestProperties.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("custom.properties"); //读取配置文件,指定读取编码 UTF-8,防止内容乱码 prop.load(new InputStreamReader(in, "UTF-8")); //获取 Properties 中全部的 key 元素 Enumeration enProp = prop.propertyNames(); while (enProp.hasMoreElements()){ String key = (String) enProp.nextElement(); String value = prop.getProperty(key); System.out.println(key + "=" + value); } }
输出内容如下:
userPwd=123456
userEmail=123@123.com
userAge=18
userName=李三
userGender=男
总结
Properties 继承自 Hashtable,大部分方法都复用于 Hashtable,比如,get、put、remove、clear 方法,**与 Hashtable 不同的是, Properties中的 key 和 value 都是字符串,**如果需要获取 properties 中全部内容,可以先通过迭代器或者 propertyNames 方法获取 map 中所有的 key 元素,然后遍历获取 key 和 value。
需要注意的是,Properties 中的 setProperty 、load 方法,都加了synchronized同步锁,用来控制线程同步。
03. properties 文件的加载方式
在实际开发中,经常会遇到读取配置文件路径找不到,或者读取文件内容乱码的问题,下面简单介绍一下,properties 文件的几种常用的加载方式。
properties 加载文件的方式,大致可以分两类,第一类是使用 java.util.Properties 的 load 方法来加载文件流;第二类是使用 java.util.ResourceBundle 类来获取文件内容。
在src/recources目录下,新建一个custom.properties配置文件,文件编码格式为UTF-8,内容还是以刚刚那个测试为例,各个加载方式如下!
通过文件路径来加载文件
这类方法加载文件,主要是调用 Properties 的 load 方法,获取文件路径,读取文件以流的形式加载文件。
方法如下:
Properties prop = new Properties(); //获取文件绝对路径 String filePath = "/coding/java/src/resources/custom.properties"; //加载配置文件 InputStream in = new FileInputStream(new File(filePath)); //读取配置文件 prop.load(new InputStreamReader(in, "UTF-8")); System.out.println("userName:"+prop.getProperty("userName"));
输出结果:
userName:李三
通过当前类加载器的getResourceAsStream方法获取
这类方法加载文件,也是调用 Properties 的 load 方法,不同的是,通过类加载器来获取文件路径,如果当前文件是在src/resources目录下,那么直接传入文件名就可以了。
方法如下:
Properties prop = new Properties(); //加载配置文件 InputStream in = TestProperties.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("custom.properties"); //读取配置文件 prop.load(new InputStreamReader(in, "UTF-8")); System.out.println("userName:"+prop.getProperty("userName"));
输出结果:
userName:李三
使用ClassLoader类的getSystemResourceAsStream方法获取
和上面类似,也是通过类加载器来获取文件流,方法如下:
Properties prop = new Properties();//加载配置文件InputStream in = ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream("custom.properties");//读取配置文件prop.load(new InputStreamReader(in, "UTF-8"));System.out.println("userName:"+prop.getProperty("userName"));
输出结果:
userName:李三
使用 ResourceBundle 类加载文件
ResourceBundle 类加载文件,与 Properties 有所不同,ResourceBundle 获取 properties 文件不需要加.properties后缀名,只需要文件名即可。
ResourceBundle 是按照iso8859编码格式来读取原属性文件,如果是读取中文内容,需要进行转码处理。
方法如下:
//加载custom配置文件,不需要加`.properties`后缀名 ResourceBundle resource = ResourceBundle.getBundle("custom"); //转码处理,解决读取中文内容乱码问题 String value = new String(resource.getString("userName").getBytes("ISO-8859-1"),"UTF-8"); System.out.println("userName:"+value);
输出结果:
userName:李三
“Properties如何使用”的内容就介绍到这里了,感谢大家的阅读。如果想了解更多行业相关的知识可以关注网站,小编将为大家输出更多高质量的实用文章!
内容来源网络,如有侵权,联系删除,本文地址:https://www.230890.com/zhan/150503.html
